The first category Power Electronics Circuits are Diode Rectifiers which is also called Uncontrolled Rectifiers. These kind of Rectifiers are uncontrollable; means their output
First of all, let us discuss
 |
There are two modes of Diode Operations:
Reverse Bias:
If diode negative terminal battery Positive terminal reigon P-N reigon doesnt
Summary: No conduction in Reverse Bias Manner
Forward Bias:
If diode with battery path
Summary: Diode will conduct current but with 0.7 constant drop on
Types of Rectifier (In Output Terms):
1. Half wave Rectifier
2. Full Wave Rectifier
Half Wave Rectifier:
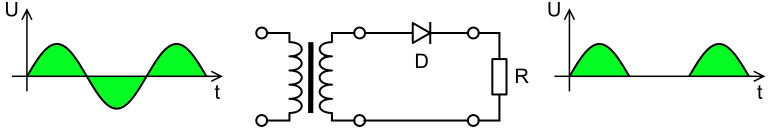 As the name suggests in this type of Rectifier output of wave is only Half Wave of
As the name suggests in this type of Rectifier output of wave is only Half Wave of Vavg= 0.316 x
Vp= Peak value of AC signal
Full Wave Rectifier:
 In this type full AC signal is converted to DC even negative signal is made positive by means of Rectification, there are many circuits to do this, but two famous ones are Bridge Rectifier and Centre tap Transformer as you can see in the figure.
In this type full AC signal is converted to DC even negative signal is made positive by means of Rectification, there are many circuits to do this, but two famous ones are Bridge Rectifier and Centre tap Transformer as you can see in the figure.Other circuit for Full wave is Bridge Rectifier as we can see its
Average Value of Full Wave Rectifier can be calculated same as Half Wave, but its period will be taken π instead of 2π.
Problems in Rectification:
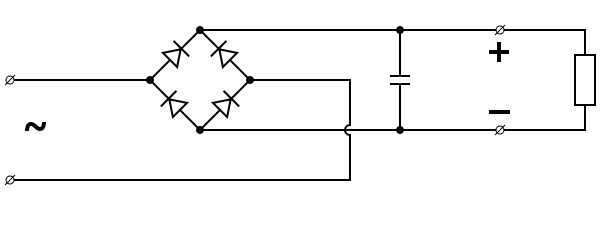 One of the problems with this type of rectification is that
One of the problems with this type of rectification is that Summary:
As you can see rectification is done by simple diodes, but output can only be depended upon input, we can't control output by any gate or some sort of anything, so

Post a Comment
Please give us feedback in comments here