 |
| Basic Symbol for Thyristor. |
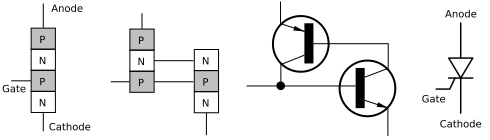 |
| As you can see it is made from connecting to PN Junction or it can Also be made from a PNP and A NPN transistor |
Types of Thyristor:
There are two types of Thyristors in terms of Direction of current flowing through them
- Unidirectional
- Bidirectional (TRIAC)
Unidirectional Thyristors are Further Divided
- SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier)
- LASCR (Light activated Silicon Controlled Rectifier)
We will only be discussing SCRs and their Turn ON and Turn OFF Techniques in this post.
 SCR is Three Terminal
SCR is Three Terminal There will be slight Leakage Current, This stage of SCR is called Forward Blocking State or Leakage State.
If Anode to Cathode voltage is increased significantly
 |
| On Positive X-axis |
As we can see the V I Characteristics of Thyristor
I'h= Holding Current
I L= Latching current
The Anode Current must be more than the value of I L i.e Latching current otherwise
Since a
Thyristors Turn ON Techniques:
There are following techniques through which
- Applying Gate voltages
- Anode Voltage > Vbo
- Thermal Energy
- Large
dV dt - Optically
( Specifically in
Large dV dt
Commutation(
It is a process of turning off a thyristor circuit
Types of Commutation:
There are many types of commutation it
- Natural
Commutaion - Forced commutation
Forced is further divided into two types
- Resonant
- Impulse Commutation
1- Natural Commutation:
Natural commutaion process turn biased then thyristor have to turn it on again by firing at Gate
2- Forced Commutation:
In some Application the input voltage is DC and hence there is no Zero Crossing of the current is possible. In these types of circuits the forward current ofthyristor is forced to zero by an additional circuitry , forced commutation can be acheived by following methods:
Resonant/ Self Commutation:
In some Application the input voltage is DC and hence there is no Zero Crossing of the current is possible. In these types of circuits the forward current of
Resonant/ Self Commutation:
In this circuit value of L and C must be chosen such that we acheive an underdamped circuit, due to this underdamped circuit the oscillating current will start flowing and SCR will be turned off at zero Crossing.
You can ask anything that you aren't able to understand. Please Give us feedback and Ask us.
You can ask anything that you aren't able to understand. Please Give us feedback and Ask us.


Post a Comment
Please give us feedback in comments here